Solid State Media Storage

Here you will learn various Solid State Media storage devices.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
Solid State Drives are rapidly taking over HDDs. They do not have any moving parts.
- No reels of tape, no spinning disks, no moving laser beams, etc.
- Solid State Storage technology is known as ‘Flash Memory’ and examples include Memory Sticks, Pen drives and Memory Cards.
- They store data as 1s (ones) and 0s (zeros) (just like magnetic and optical storage devices) within millions of mini transistors instead of on films of magnetic substance, which is collectively called as a NAND chip. If the transistor conducts an electric current, this equates a 1. If it does not conduct a current, this equates a 0 (zero).
Advantages
- They hold several advantages over magnetic disk drives.
- Smaller physical size and also considerably lighter than HDDs
- Consume much less power (No moving parts to use energy).
- Much faster data access/transfer times.
- More robust (No moving parts that makes them harder to damage).
- They run much cooler than HDDs.
Memory Stick/pen drives/USB media
Memory sticks/pen drives/USB media are small portable external storage devices.
- Can be used to transfer/backup many GB of data/files between computers.
- They use Solid State technology and are usually connected to the computer via USB ports.
- These are making other forms of portable storage (like CD’s and DVD’s) redundant as they are simply much easier and quicker to transfer data.
- Data can be quickly read (used) or written (update) to the drive.
- Memory sticks used be very expensive initially but they have become very cheap now.
- Some expensive software now use these storage methods as a form of security. They plug into the computer using the USB port and are known as dongles. The software installed on a computer sends out a request in encrypted form to the dongle asking for an encrypted validation key. Thus, a person trying to carryout out software piracy needs to break the code on the dongle first before he/she could use the software. This gives an added security to the software.
USB Media
Uses
- Used for easily transporting files or data between PCs.
- Used for backing up data quickly and easily.
- Can be used as a security device (a dongle) to prevent software piracy.
Advantages
- Very small and easy to transport data.
- Robust and not easily damaged (no moving parts).
- Work in any PC using USB connectivity.
- Not affected by magnetic fields.
- Does not need any additional software to work on most computers.
Disadvantages
- No write protect feature. This means that it is possible to accidentally copy over data.
- Small physical size means that they are easy to misplace or lose.
- User needs to be very careful when removing a memory stick from the computer as incorrect removal say while it is still doing a read/write operation, will corrupt the data on the memory stick, rendering it useless.
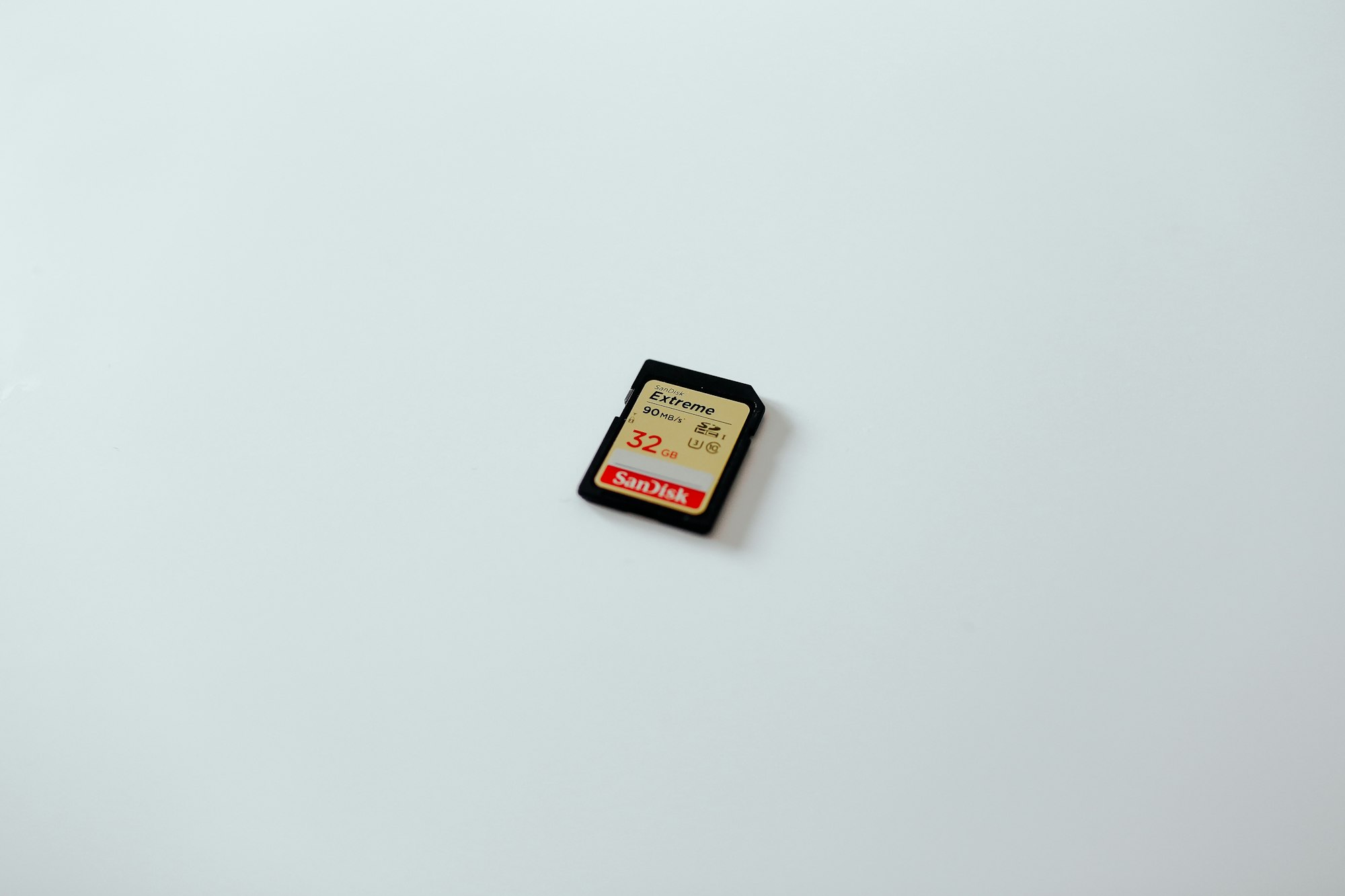
Flash Memory Cards
These a form of electronically erasable programable read-only memory (EEPROM) and are examples of solid state memories.
Flash Memory Card
Uses
- Used as mobile phone memory cards.
- Used in MP3 players to store music files.
- Used as a backup store in hand-held computer devices
- Storing photos on digital cameras.
Advantages
- Since they are solid state memories, they are very robust.
- Very compact and can be easily removed and used in another device or transferring photos directly to a computer or printer.
Disadvantages
- Expensive per gigabyte of memory when compared to hard drive disks.
- Have a finite life regarding the number of times they can be read from or written to.
- Have a lower storage capacity than hard disks.
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!