Plant Nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is taking in useful substances. You may recall that nutrition is one of the characteristic of a living thing and therefore it is important that living things take in useful substances ideal for their growth using nutrition.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light is called as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is extremely important in the plant’s nutrition.
Photo: Light
Synthesis: Manufacturing of chemical compounds
Chlorophyll- the plant power station
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that is inside a chloroplast molecule.

When the sun shines on a chlorophyll molecule:
- Some of the energy in the light is absorbed by it
- The chlorophyll molecule then releases the trapped energy
- The released energy makes carbon combine with water
- This is done with the help of enzymes in the chloroplast
- This causes glucose to be made
- The glucose contains energy from the light
- Thus the light energy is converted into chemical energy in photosynthesis.
The equation for photosynthesis
Word equation: Carbon dioxide + water + energy from light → glucose + oxygen
Chemical equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O + (energy) → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Leaves- the Plant's Nutritionists

A leaf contains palisade cells, which contains chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll molecules, which contain the enzymes that catalyse photosynthesis! Marvellous right?
Parts of a Leaf
| Leaf Part 🌿 | Function(s) ⚙️ |
|---|---|
| Epidermis (upper) | - Doesn't contain chloroplasts - Secretes a waxy substance called the Cuticle that covers the upper epidermis. |
| Waxy Cuticle | Helps in lowering transpiration rates ☀️ |
| Epidermis (Lower) |
- Has small openings called stomata - Stomata protect inner layers of cells and help in the gas exchange of the leaf |
| Guard cells 👮♂️ | Controls the movement of substances in and out of the stomata |
| Palisade Mesophyll Cells | Contains many Chloroplasts 💚 as compared to other cells in the plant, to carry out photosynthesis |
| Spongy mesophyll cells | Have air spaces that facilitate the diffusion of Carbon dioxide through the cell wall and cell membrane of each cell |
| Xylem tube | Carries water to the Mesophyll Cells 🌊 |
| Phloem tube | Takes away substances that the leaf has made such as Sucrose. |

Adaptations of a Leaf
| Adaptation | Function(s) |
|---|---|
| Stem and Petiole support 🌱 | Exposes most of the leaf's surface to Sunlight and Air |
| Large surface area | To expose the cells to the largest amount of Sunlight as possible |
| Thin layered | - Allows sunlight to reach all cells - Allows Carbon Dioxide to diffuse in and Oxygen to diffuse out |
| Palisade cells are arranged end on (vertically) |
Keeps as few cell walls as possible between Sunlight and Chloroplasts 🟩 |
| Chloroplasts arranged broadside on (horizontally) |
Exposes optimum amount of chlorophyll to Sunlight |
| Chlorophyll 💚present in cells in the Mesophyll layer |
Absorbs energy ⚡️from Sunlight so that Carbon Dioxide combines with Water |
| No Chloroplasts in Epidermal layer |
Allows Sunlight to reach cells in the mesophyll layer |
| Stomata in lower epidermis | - Allows Carbon Dioxide to diffuse in - Allows Oxygen to diffuse out |
| Air spaces in Spongy Mesophyll | Allows Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen to diffuse In and Out of the cells during photosynthesis |
| Chlorophyll arranged on flat membranes inside chloroplasts |
Exposes maximum amount of chlorophyll to sunlight 🌞 |
| Xylem vessels within short proximity of mesophyll cells |
Supplies water to the Mesophyll cells for Photosynthesis |
| Phloem vessels within short proximity of mesophyll cells |
Carries away Sucrose and other organic products of Photosynthesis |
Uses of Glucose in the Plant’s Nutrition
| Use(s) | Notes |
|---|---|
| Used for Energy ⚡️ | Energy can be released from glucose using Aerobic respiration. |
| Used to make Proteins | Nitrate molecules are mixed with glucose to form strands of amino acids which are bound into Proteins |
| Used to make organic substances |
Organic substances such as: Sucrose, Cellulose, Chlorophyll, (using nitrogen and magnesium), Fats Oils, etc can be made |
| Transformed to Sucrose for transport 📦 |
Sucrose is less reactive, has small sized molecules, is soluble in Sap and hence can be transported in phloem vessels |
Storing Glucose
Glucose is stored as starch (and not as glucose) because:
- Glucose is reactive, may indulge in unwanted chemical reactions in the cells and .
- It is a small molecule, and is also soluble in water, and thus might be lost from plant cells when dissolved in water
- It may increase the glucose concentration in the cell and cause damage.
Glucose is stored as Starch because:
- Starch is an unreactive large molecule
- In comparison to Glucose, Starch is not very soluble, and can be broken down or stored inside chloroplasts.
Mineral ions required by plants
| Element | Mineral ion | Function | Deficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Nitrates OR Ammonium ions | To build proteins | Weak growth, Yellow leaves |
| Magnesium | Magnesium ions | To make chlorophyll | Yellowing between veins of the leaves |
Limiting Factors
A limiting factor is something present in the environment in such short supply that it restricts life processes. This means that nutrition is restricted at a certain level and the plant is at its peak of growth!
Here is a list of some limiting factors you need to know:
| Limiting factor | Notes |
|---|---|
| Sunlight 🌞 | - As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis will increase as well - But at a certain point, even if the light gets brighter, the rate of photosynthesis will not increase. |
| Carbon dioxide 💨 | The more the carbon dioxide concentration increases, the more the photosynthesis rate, until a maximum limit is reached. |
| Temperature 🌡 | A plant photosynthesises at a greater rate when temperatures are warmer, in comparison to colder temperatures. |
| Stomata 🟢 | - If the stomata are closed, then photosynthesis cannot take place - On a warm, sunny day, stomata often close to decrease transpiration rates. - Hence this can lead to low photosynthetic rates. |

Glasshouses- the tools to maximise nutrition
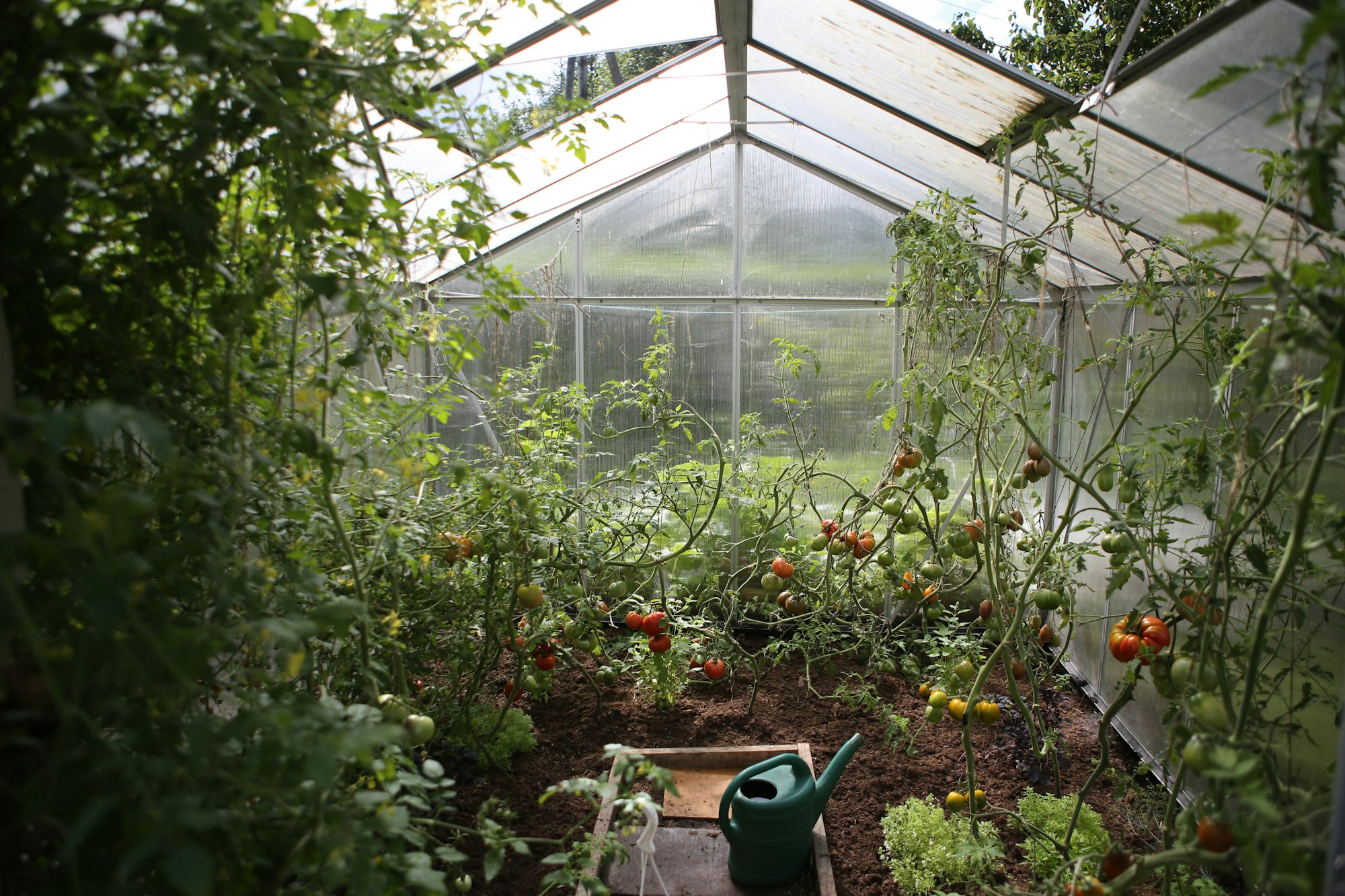

Plants can be grown in glasshouses where environmental conditions can be controlled and hence the plant’s nutrition can be enhanced.
These environmental conditions include:
- Light
- Temperature
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Soil pH
- Moisture (and water)
Light
A range of light intensities can be provided at the correct wavelengths to the plant even in cloudy and dark conditions.
Temperature
The temperature of the glasshouse can be controlled with heating and cooling equipments, so that the plant gets an optimum temperature to photosynthesise
Carbon dioxide concentration
As the natural carbon dioxide concentration is very low (0.04%) plants cannot photosynthesise at greater rates; whereas, in a glasshouse, it is possible to control carbon dioxide concentrations.
Importance of photosynthesis
- Brings the energy of sun into ecosystems
- Essential for maintaining a constant global level of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- Helps to stop level of carbon dioxide to rise too high
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!
Next Topic