Networks and their terminologies

Learn about the various terminologies used in Networks and which are in fact the backbone of networks.
We will see what is LAN, WAN, WI-FI, Bluetooth and their differences. In the end, we will also how to setup a small LAN.
Difference between IP address and MAC address
A MAC address is a unique number that identifies a device connected to the internet.
Now let us understand the difference between an IP address and a MAC address.
The IP address gives the location of a device on the internet, whereas the MAC address identifies the device connected to the internet.
You can think of the IP address as the computer's street address. Just as the post office knows to deliver your mail to your street address, the internet knows how to send the correct data to the correct computer by the IP address.
Using this example, the MAC address can be thought of as a way of uniquely identifying each person living in your house. It is possible that you move to a new house (so your IP address will change) but the same people will be living in the new house (so their MAC address will remain unchanged).
How computers use Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to connect to networks
Both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer wireless communication between devices. They both use radio frequencies as the carrier of data transmission.
Wi-Fi
A wireless transmitter (WAP) receives information from a network via its connection, e.g., a broadband connection if internet is used. This transmitter converts the received information into radio waves via an installed wireles.
- WiFi refers to any system, where it is possible to connect to a network or to single computer through wireless communication. E.g., Laptop computers which are wifi enabled can connect to devices like printer, keyboard, etc.
- Wifi system rely on some form of access point (AP) or hot spot, which uses radio frequency technology to enable the device to receive and send signals. The range of a hot spot is upto 100 metres.
- It is not a short form of wireless Fidelity. It is a trademark name for any product which is based on IEEE 802.11 standard.
- A device (computer or smartphone) receives the radio waves via an installed wireless adaptor which allows it to download the information from the data source. This works in reverse when the device wishes to transmit data over the network.
- Wifi hotspots are places where you can access wifi (free or paid).
- They exist in public places such as airports, hotels, internet cafes’, etc.
- It is possible to log on to free wifi unless they are protected by password.
- Software exists which can be loaded in a laptop which then searches for non protected wifi system. The practice of driving around in a car looking for these unsecured wifi hotspot is known as war driving and possess a security risk.
Bluetooth (Personal Area Network)
Bluetooth is a wireless network technology designed for very short range connections (just a few metres). Bluetooth sends and receives radio waves in band of 79 different frequencies (known as channels). They all work around 2.45 GHz frequency.
Devices using Bluetooth automatically detect and connect to each other, but they don't interfere with other devices since each communicating pair uses a different channel (from the 79 options).
When a device wants to communicate, it picks one of the 79 channels at random. If the channel is already being used, it randomly picks another channel. This is known as spread-spectrum frequency hopping.
To further minimise the risks of interference with other devices, the communication pairs constantly change the frequencies or channels they are using, several times a second.
- The idea of bluetooth is to get rid of all those cables, that connects our computer to peripheral devices such as printers, mouse, keyboard, etc.
- Bluetoowith devices contain small, low power, radio transmitters and receivers.
- When devices are in range of bluetooth devices, they detect each other and can be connected.
- With this system, it is possible to create small home networks.
- The range is however quite small (about 10 metres).
Typical uses of Bluetooth
- Connecting a wireless keyboard to a computer.
- Connecting a wireless mouse to a computer.
- Using a wireless headset with a mobile phone.
- Printing wirelessly from a computer or PDA.
- Transferring data or music from a computer to a MP3 player.
- Transferring photos from a cell phone or camera to another device.
Bluetooth creates a secure wireless personal area network (WPAN) based on key encryption.
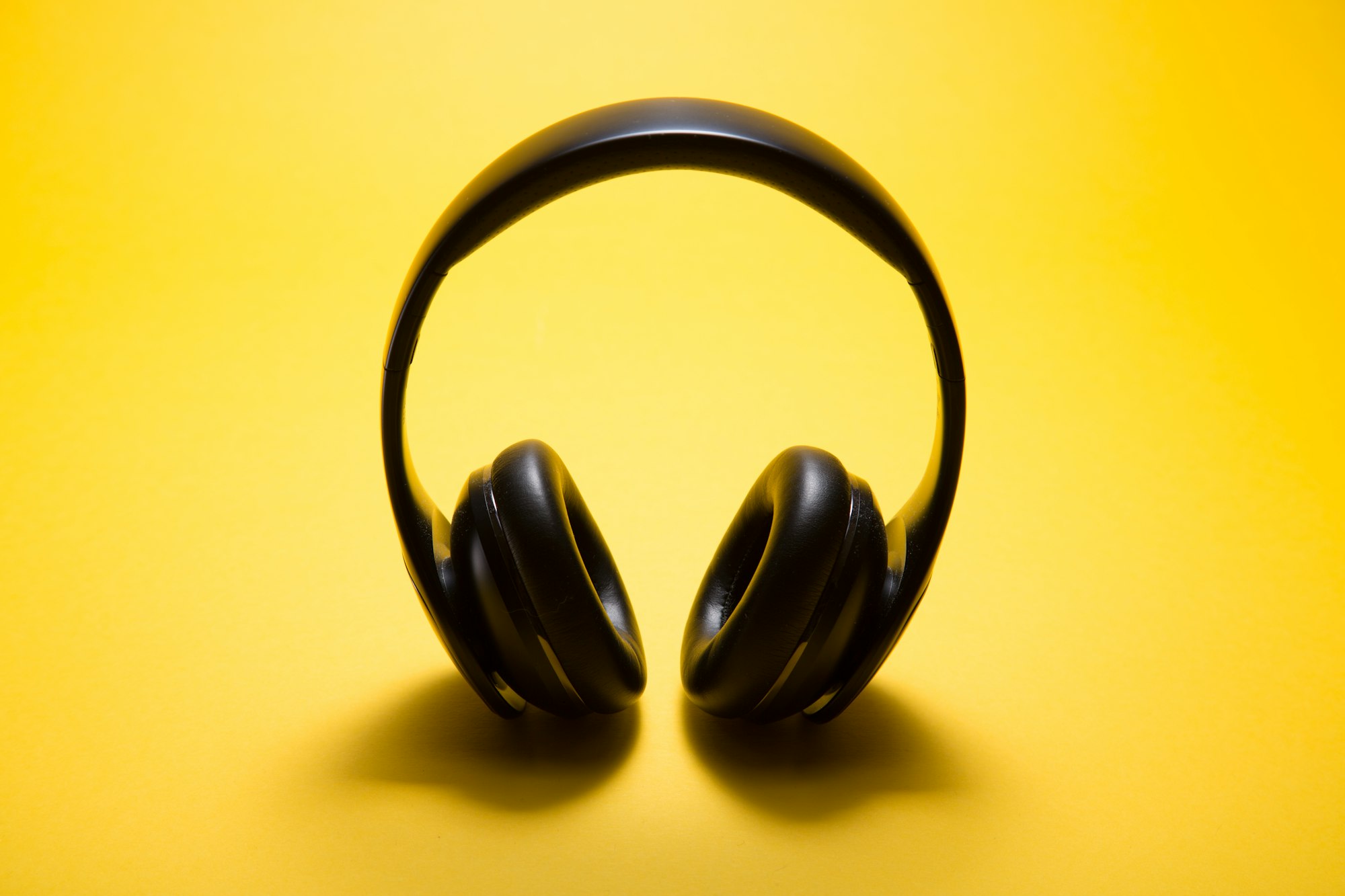
A Bluetooth Headphone
| Feature |
Bluetooth |
Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission frequency used |
2.4GHz |
2.4, 3.6, 5.0 GHz |
| Data transfer rate (maximum) |
25 Mbits/second (~3.1 Mbytes/second) |
250 Mbits/second (~31 Mbytes/second). |
| Maximum effective range (metres) |
10 metres |
100m (but can be obstructed by walls etc., reducing effective range to only a few metres). |
| Type of data transmission security |
Key matching encryption |
WEP (wireless equivalent privacy) and WPA (Wi-Fi protected access) are the most common security systems. |
| Maximum number of devices connected |
Up to 7 |
Depends on the router used (can be one device or many devices). |
How do you setup and configure a small network
If you want to set up a small network, you will need the following hardware and software
Hardware
- One or more switches or hub, tooling devices together.
- Network cables to connect devices to the switch.
- A separate wireless access point to allow wireless devices to connect to the network. E.g. Laptops, smartphones, etc.
- A router to connect your LAN to the WAN.
- A firewall to protect your network from the hackers.
- A bridge is required if you already have a section of the network and you want new network to connect to it.
- Servers to manage network functions such as network security, shared resources like network file storage, etc.
You would also need to organise some other things like:
- Set up an account with an ISP.
- Get an internet connection installed from the ISP, to install your line in your location.
- Configure various bits of hardware and software so that everything works with the network.
- Install all the common softwares in a server and also making sure that a network licence has been acquired so that all network users can make use of the software.
- Setting up roles and responsibilies for the users so that each user can only access their own area or common shared area.
- Setting up of a network-level of privilege so that the netowrk administrator can monitor network usage, change passwords, etc.
Software
- Web browser to access internet.
- Firewall – if it is software.
- Anti virus to protect your network
What are the types of Network?
There are three types of Networks:
- LAN – Local Area Network
- WLAN – Wireless Local Area Network
- WAN – Wide Area Network
What is a LAN?
Local Area Network or LAN is usually within one building or not over a large geographical area. A LAN consists of a number of computers and devices, e.g., printers, which will be connected to hubs or switches.
One of the hubs or switches will usually be connected to a router and a modem (generally broadband to allow the LAN to connect to the internet; in doing so it then becomes part of a WAN.
Advantages
- The sharing of resources (such as expensive peripherals and application software).
- Communication between users.
- A network Administrator to control and monitor all aspects of networking. E.g., Changing password, monitoring internet, etc.
Disadvantages
- Easier spread of viruses through the whole network.
- The development of queues for printer, which can be frustrating.
- Slower access to networks, such as internet.
- Increased security risk as compared to stand alone computers.
- If the main server breaks down, in must cases, the network will no longer function.
What is a WLAN?
Wireless Local Area Networks or WLANs are similar to LANs, but there are no wires or cables. They provide wireless network communication over very short distances (a few metres) usually radio or infra-red signals instead of cables.
Devices known as access points (APs) are connected into the wired network at fixed locations. Because of the limited range, most commercial WLANs need several access points, to permit uninterrupted wireless communication.
APs use either spread spectrum technology which is a wideband radio frequency with a range of about 30-50 metres or infrared, which has a short range of 1-2 metres and is easily blocked and therefore has limited use.
The access point receives and transmits data between the WLAN and the wired network structure. Ens users access the WLANs through wireless LAN adapters that are built into the devices or are a plug-in module.
Advantages
- All computers can access the same services and resources. E.g., printers, scanners, internet access, etc.
- There is no cabling to individual computers and devices, so safety is improved.
- The system is more flexible since, users can move their laptops from their desks.
- Adding new computers and devices is a very easy task and costs are reduced, since no extra cabling is needed.
Disadvantages
- Security is a big issue, since anyone with a WLAN enabled laptop or computer, can access a network if it can pickup a signal.
- There may be problems of interference, which can affect the signal.
- Data transfer is slower than LAN.
What is Wide Area Network (WAN)?
A Wide Area Network is formed by a number of LANs being connected together through either a router or modem. Some companies setup private WANs. This is expensive but comes with an advantage of much enhanced security and speed. It is common to use an Internet Service Provider (ISP) for connections to the internet and communicate through this network system.
The most common examples of WAN are the internet and the network of ATMs used by banks.
Advantages
- A WAN is a network that extends over a large area.
- WAN can be connected using optical fibre cables, satellite links, radio signals, etc.
Disadvantages
- They are very expensive.
- Limited access.
- Data access slows down if spread over huge area.
Write the difference between LAN and WAN
| Sr No | LAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN is confined to a very small area. | WAN covers wide geographical areas. E.g. Between cities, countries and even continents. |
| 2. | Usually located in a single building. | Usually located between many buildings and countries. |
| 3. | Uses cables, wireless, infra-red which are usually queued by the organisation. | It uses wireless, satellite links, which are globally organised. |
| 4. | We can restrict or block any websites. | WAN has very fast speed. |
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!