Movement in And Out of Cells
In this section of IGCSE Biology, we shall be covering Diffusion and Osmosis topics.
Diffusion
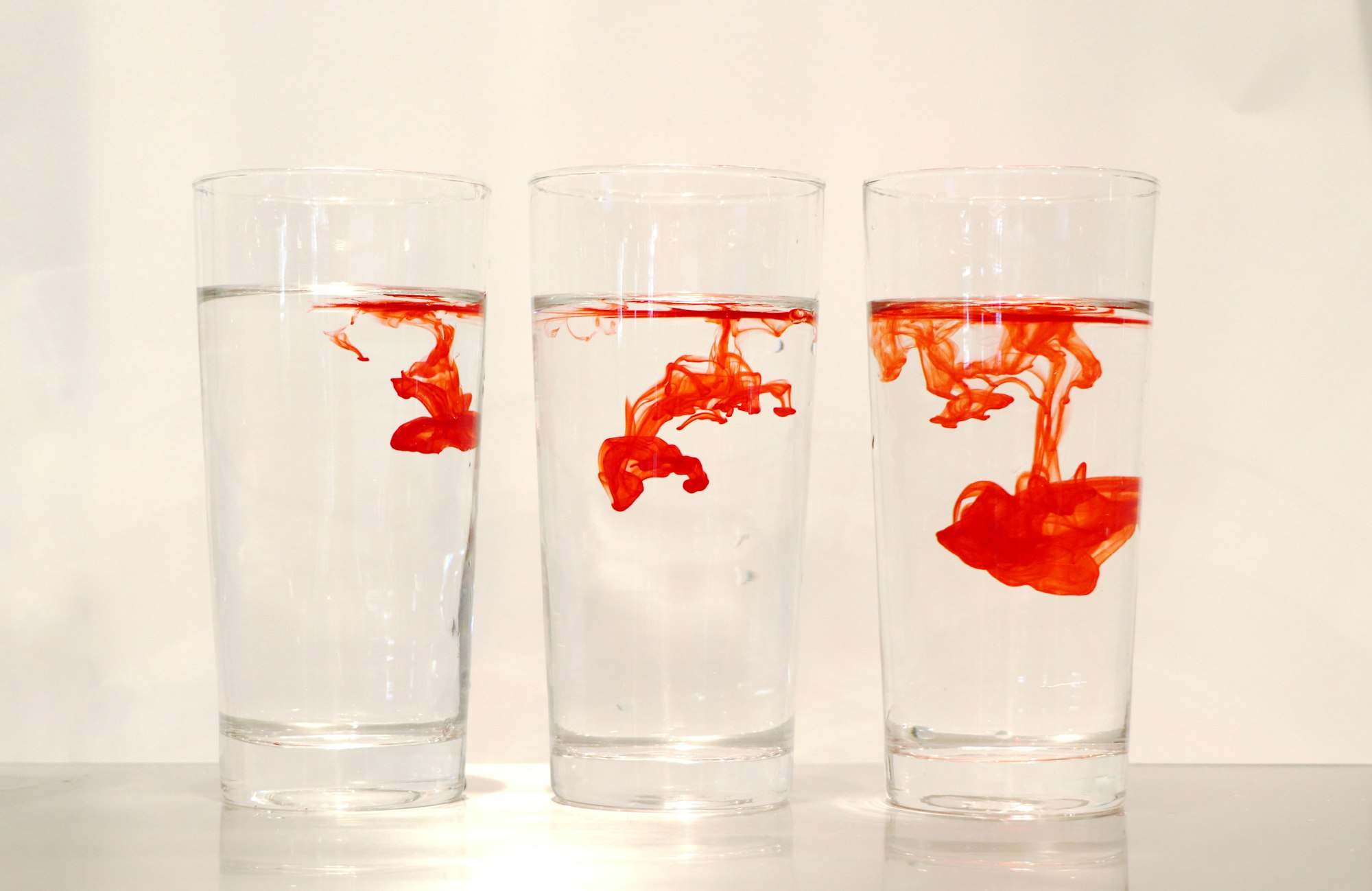
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules and ions from a region of higher concentration, to a region of lower concentration, as a result of their random movement.

Let’s consider an example:
You are spraying an air freshener in the air and soon you realise that the scent has spread all over the room. The mixture in the air freshener bottle is the region of higher concentration, and the room is a region of lower concentration. So the differences in the concentration gradients is what that causes diffusion.
Diffusion in cells
When a living cell such as a plant or an animal cell is considered, there is an obstacle that can affect diffusion: A partially permeable cell membrane which controls the movement of substances.
Importance
Diffusion is needed by living organisms for:
- Obtaining necessary requirements needed for metabolism
- Getting rid of waste and toxic substances
Examples:
- Plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis; carbon dioxide is just 0.04% in the atmosphere, but still there is lesser volume of it in the plant cells. So the atmosphere is the region of higher concentration and the leaves are regions of lower concentration.
- The same example of the leaf can be used with oxygen, which is a waste product for the plant. Oxygen diffuses from it’s region of production (higher concentration) to the atmosphere where it is scattered (lower concentration)
- Diffusion is also used by insect pollinated flowering plants to send out the scent of the nectar they produce to attract insects.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules from a region of high water potential (region which has more water molecules) to a region of low water potential (region which has less water molecules), down the concentration gradient, through a partially permeable cell membrane.

Partially permeable membranes
As described previously, partially permeable membranes are those which restrict the passage of molecules which exceed a particular size.
Cell membranes play a pivotal role in Osmosis as only water molecules are allowed to pass through the cell membrane.
Visking tubing is an artificial form of the natural cell membrane.
Osmosis in animal cells
In concentrated solution (Low water potential)

- Animal cells shrink as they have a higher water potential than their surroundings
In dilute solution (High water potential)

- Animal cells burst as their surroundings have a higher water potential than them and water enters their cells up to such an extent that their cell membranes burst
Osmosis in plant cells
In concentrated solution (Low water potential)

- Plant cells plasmolyse as they have a higher water potential than their surroundings
In dilute solution (High water potential)

- Plant cells become turgid, but do not burst, as they have a supportive cell wall that is tougher than their cell membrane.
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!
Next Topic