Input Devices - Input Card Readers, Sensors and Remote Control
Here we will study magnetic stripe readers, contactless card readers, chip and pin readers, RFID readers, sensors and remote control as part of Input Card Readers, Sensors and Remote Control.
What are Input Card Readers?
Let's study these readers in detail one by one.
Magnetic Stripe Reader (MSR)
Many cards such as credit cards and debit cards have a stripe of materials that can be magnetized on the back side.
Data can be stored here in the form of magnetized dots.
Usually the data stored on this stripe or strip is the same data that is shown on the front of the card.
For example:
- Credit card number
- Credit card holder’s name
- Start date
- Expiry date, etc
The strip allows the data to be input into the computer system, faster and with more accuracy than typing it in.
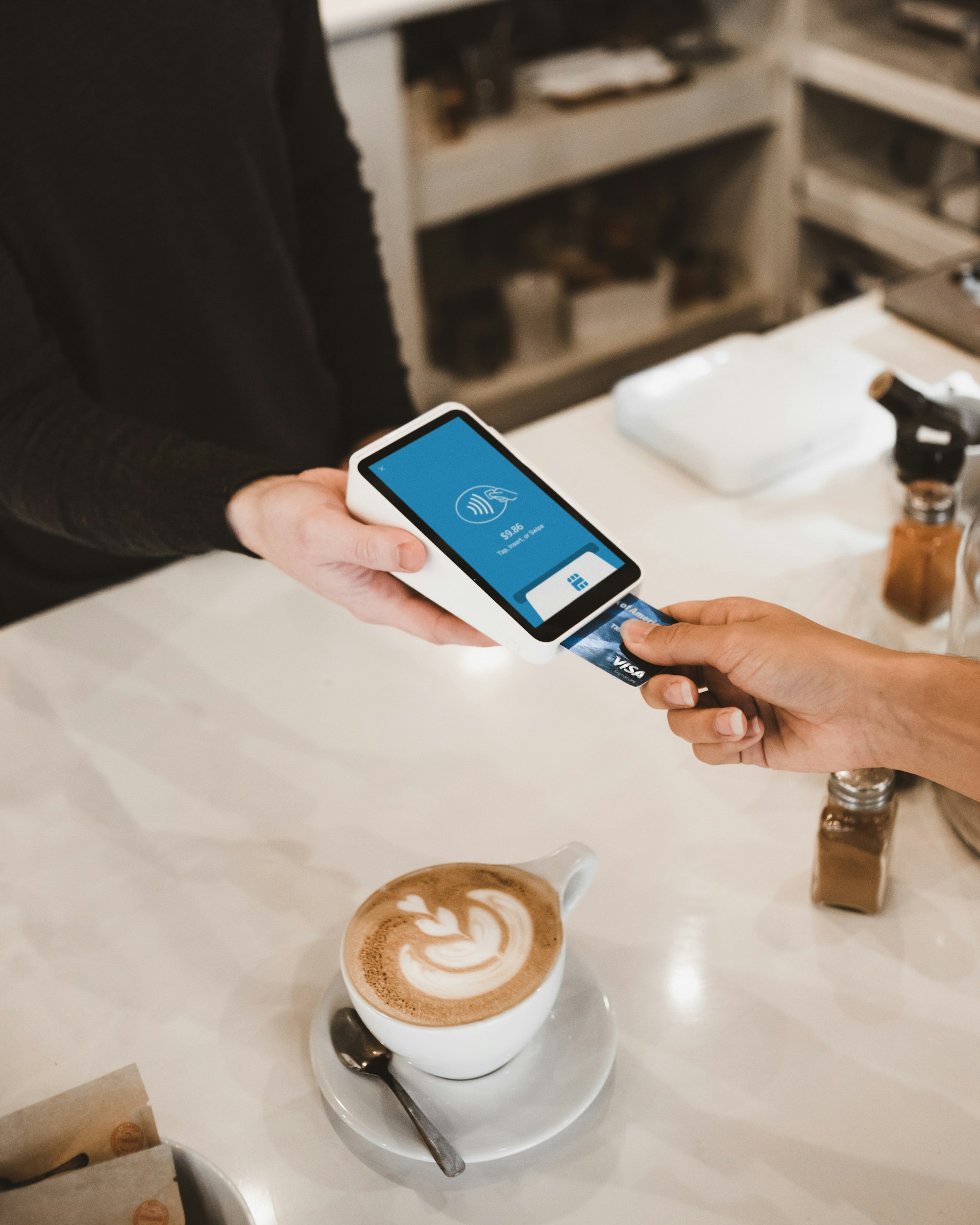
MSR is used to read data from the strip. This can be done by swiping the card through a slot on the reader.
Credit/Debit card with Reader
Uses
- On credit/debit cards for use at ATMs or EFTPOS (electronic funds transfer at point of sale) terminals.
- Security devices to allow entry to buildings, hotel rooms, etc.
Advantages
- Data can be entered more quickly by swiping the card rather than typing in manually.
- The magnetic strips are not affected by water, oil or moisture; hence they are robust.
- Usage of MSR avoids possible typing errors.
- Secure as the data is not in a human readable form and since there is no typing, removes the risk of somebody observing your keystrokes.
- Prevents access to restricted/secure areas.
- No moving parts, so physically robust.
Disadvantages
- Magnetic strips can only store a small amount of data.
- Magnetic strips can be easily damaged by magnetic fields.
- The cards cannot be read at a distance, as you have to put them in the reader and swipe them.
- As the information is not human readable, this can be a disadvantage in some applications.
Contactless card readers
Contactless debit or credit cards allow customers to pay for items worth up to a certain amount without entering their PIN. All contactless cards have a small chip that emits radio waves embedded in them. The card is held within a few centimetres of the payment terminal to pay for an item; the terminal picks up the signal from the chip and allows the transaction to be processed.
The steps are as follows:
- Customers look out for the contactless symbol on the payment terminal.
- The shop assistant enters the amount for payment.
- The card reader informs the customer to present their contactless card.
- The customer holds their card in front of the card reader.
- The terminal display will indicate that the card has been read.
Debit card with built-in chip and contactless transaction symbol
Advantages
- A transaction using magnetic strip reader takes 30 seconds whereas contactless card reader transaction takes 15 seconds, so transaction time is reduced.
- As the system uses 128-bit encryption, the transaction takes places securely without any compromise on data.
- Customers do not have to worry about typing errors like incorrectly typing in a PIN.
- Retailers no longer have access to the customer's credit/debit card information.
- The chip in the contactless credit card responds to the payment terminal reader with a unique number used for that transaction only; it does not simply transmit the consumer's account number, this number is also encrypted.
Disadvantages
- They are more expensive than normal credit/debit cards.
- A thief with a suitable reader could monitor your contactless card transaction while standing at the counter with you, or just behind you (the third point above reduces this risk considerably however: because you don't have to type in a PIN, somebody standing behind you couldn't steal your PIN and use it).
- Can take money twice if the customer uses it as a chip and PIN card (one is contactless and the other is chip and PIN).
- Transactions are usually limited to a small maximum value.
- Transactions have been carried out without the card holder being aware of this while they were just standing in the payment queue.
Chip and Pin readers
Modern credit cards/debit cards don’t use a magnetic strip; instead they have a tiny memory chip of computer memory embedded into them. Data can be stored in this chip and can be read by using a chip reader. A card is inserted in the reader where metal contacts to the metal pad on the front face of the card. The reader can then assess the memory chip and the data stored on it.
Smart cards can store much more data than a magnetic strip. For example, an identity smart card would not only store the owner’s name and card number, but will also have a digital image of the person.
Chip and Pin readers are generally used at EFTPOS terminals. These cards are similar to contactless cards except for two points:
- The customer has to be key in the PIN to make a transaction.
- The cards do not make use of RF technology.
Uses
- Where payments are made using cards (restaurants, supermarkets, travel agents, etc.).
Advantages
- More secure system as PIN typed in must match up with PIN stored on chip.
- More robust system than magnetic strip cards.
Disadvantages
- Prone to frauds as the user needs to ensure that PIN isn't read by somebody else while keying in the same.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) readers
This technology has already been mentioned in the description of contactless credit/debit card transactions.
Radio frequency identification (REID) readers use radio waves to read and capture information stored on a tag. The tag can be read from a distance of several metres, which is one of its advantages over the barcode RFID system. The RFID tag is made up oftwo components:
- a microchip that stores and processes information.
- an antenna that is used to receive and transmit data/information.
The tags can be passive or battery powered. Passive tags use the reader's radio wave energy to relay the information; battery powered tags use a small embedded battery to power the RFID.
Uses
- Livestock tracking so that the whereabouts of each animal on a farm is known; it also identifies which farm owns the animal.
- Retail (it is similar to barcodes but doesn't require any scanning; details, such as price, can be stored on the tag and then automatically read at a checkout — a big advantage is that several tags can be read at the same time, thus speeding up the checkout process).
- Admission passes (for example, in theme parks RFID cards eliminate the need to scan or swipe people before 'rides', reducing the waiting time; it also allows the tracking of people in the theme park and certain information, such as height or age, can be stored to prevent entry to certain rides on safety grounds).
- Libraries (books can be tracked in and out automatically by readers at the library entrance; no need to scan barcodes or magnetic stripe cards, making the process quicker and more accurate).
Advantages
- No line-of-sight contact is necessary; the tags can be read from a distance.
- it is a very robust and reliable technology.
- Very fast read rate (typically < 100 milliseconds to respond).
- Bidirectional data transfer (that is, it allows read and write operations to take place).
- Bulk detection is possible (i.e., detect several RFID tags at the same time).
Disadvantages
- Tag collision (this is when the signals from two or more tags overlap, interfering with each other).
- Because RFID uses radio waves, they are relatively easy to jam or interrupt.
- It is relatively easy to hack into the data/signal transmitted by the tag.
- RFID is more expensive than a comparable barcode system.
Explain input remote control.
Remote controls are very common in households and industries.
A signal is sent from the remote each time a button is pressed using infrared light.
Remote controls are often used to control slideshows in presentations.
A signal from the remote can even control a computer at a distance!
This feature makes remote controls to be used while controlling Television, DVD players, Air conditioning etc.
Remote controls are also used to control start and stop machinery in industries.
Remote Control controlling a television
Uses
- Televisions, satellite systems, DVD players and hi-fi systems all use remote controls to alter functions such as sound volume, on/off, change channels open the disc drawer, and so on.
- Used to control multimedia systems.
- Used in industrial applications to remotely control processes, stop and start machinery, etc.
Advantages
- Remote control enables devices to be operated from a small distance which makes it particularly useful for people with physical disabilities.
- Some chemical processes are hazardous, so it is a big advantage to be able to select operations from a distance.
Disadvantages
- Signal between control and device can be easily blocked by any obstacle.
- People with limited hand/wrist movement may find it difficult to use.
Explain Input Sensors.
A normal PC has no way of knowing what is happening in the real world around it. It doesn’t know if it is light or dark, hot or cold, quiet or noisy. A normal PC has no senses; but you can give it some by connecting sensors to it. A sensor is a device that converts a real world property (for example temperature, pressure etc.) into data that a computer can process. However, this data is in analogue form and needs to be converted to a digital form, for which an analogue to digital converter (ADC) is needed.
Advantages of using (input) sensors:
- Reading taken by input sensors are generally more accurate than those taken by human operators.
- Readings are taken round the clock; there is continuous monitoring.
- Because it is a continuous process, any necessary action or warning will be executed automatically and immediately.
- It is comparatively cheaper as compared to manually recording all readings.
- Since the monitoring is automatic, it is very useful in applications which are hazardous for humans or need precise control or monitoring.
*Disadvantages of using (input) sensors:
- Faulty sensors can give faulty results.
Give the various uses of sensors.
| Sensors | What it detects | Application (Use) |
| Temperature | Temperature change (hot/cold) | a. Central heating system |
| b. Automatic washing machine | ||
| c. Automatic greenhouses | ||
| d. Ovens | ||
| Light | Brightness (Light/dark) | a. Automatic greenhouses |
| b. Automatic doors | ||
| c. Burglar alarm systems | ||
| d. Street lighting systems | ||
| Pressure | Change in pressure | a. Automatic washing machine |
| b. Burglar alarm systems | ||
| c. Robotics | ||
| d. Environmental monitoring | ||
| Moisture/Humidity | Wetness/dryness | a. Automatic greenhouses |
| b. Factories where detecting moisture level is crucial (E.g.: Factories where soft drinks are manufactured, chip manufacturing) | ||
| c. Environmental monitoring | ||
| Water level | How full or empty a container is | Factories where soft drinks are manufactured |
| Movement | Movement | a. Burglar alarm systems |
| b. Robotics | ||
| Proximity | How close or far an object is | All industries |
| Switch or button | Anything that is pressing or touching it | Keyboard buttons |
| pH | How acidic or alkaline something is | a. Automatic greenhouses |
| b. Environmental monitoring | ||
| c. Chemical processing | ||
| Sound/acoustic | Sound of objects | a. Burglar alarm systems |
| b. Monitoring liquid and powder flow in pipes | ||
| c. Music Recording Studios |
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!