Physical Quantities & Measurement Techniques

Measurements are a part of our daily lives, right from measuring volume of edible liquids, to measuring the speed of light!
In this guide, we are going to put forward some important revision points that may come useful during your IGCSE examinations. All the very best!
Types of measurements:
- Measurement of length
- Measurement of volume
- Measurement of Time
Measurement of length
Length can be measured accurately through many methods. Here are some:
Ruler
Used to make simple measurements accurate to 0.1 cm (1 mm)

Vernier caliper
Used to make simple measurements accurate to 0.01 cm (0.1 mm)
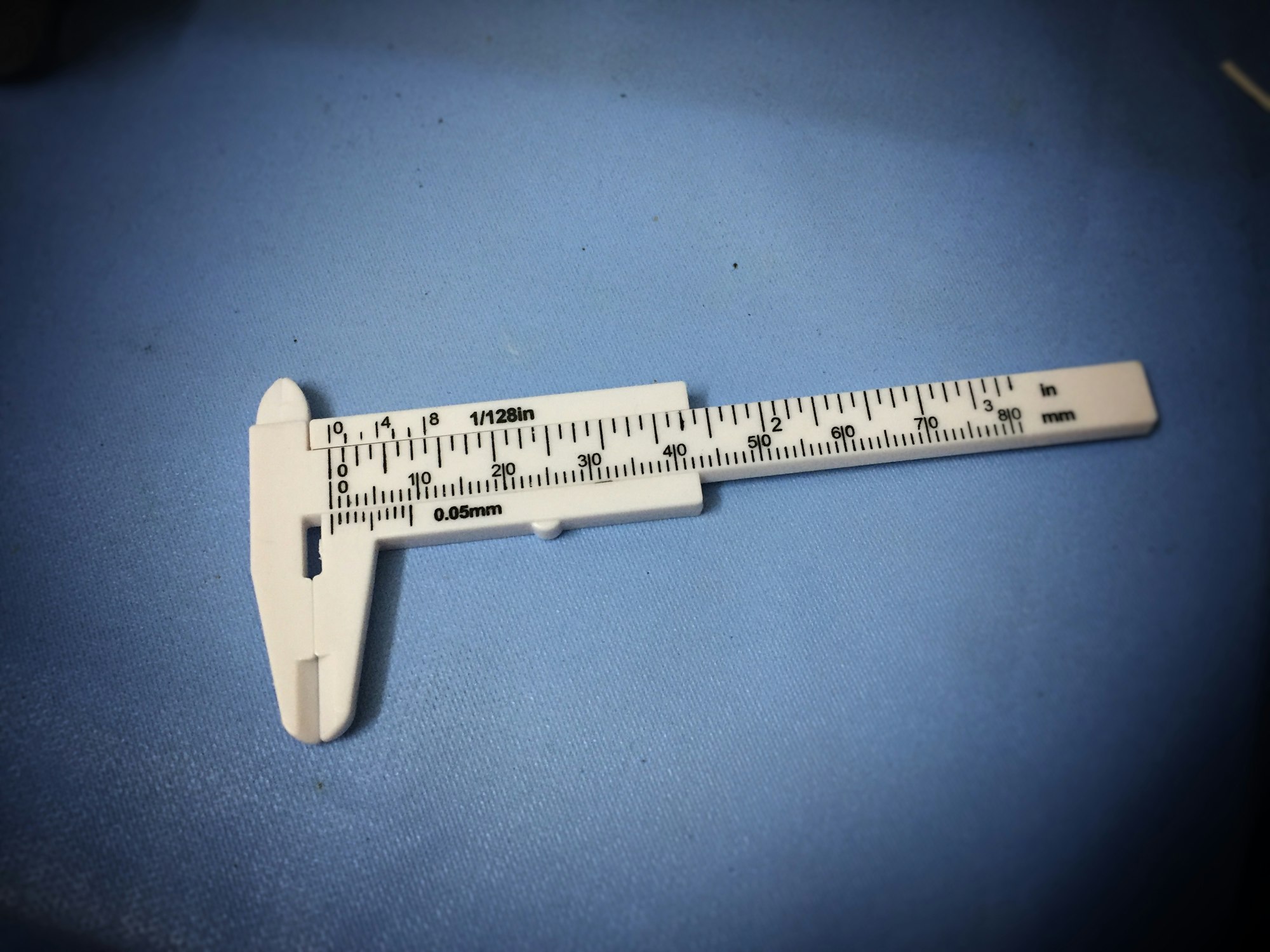

How to measure length using a vernier caliper
- Place the object between the jaws of the vernier caliper
- Measure and note the length of the object on the main scale by looking at the left of the 0 on the vernier scale.
- This tells you the length in millimeters.
- Now, observe the vernier scale;
- Find the point where one of the markings on the vernier scale is exactly aligned with one on the main scale
- This tells you the fraction of a millimeter that you must add to the main scale reading.
Micrometer screw gauge
Used to make simple measurements accurate to 0.001 cm (0.01 mm)
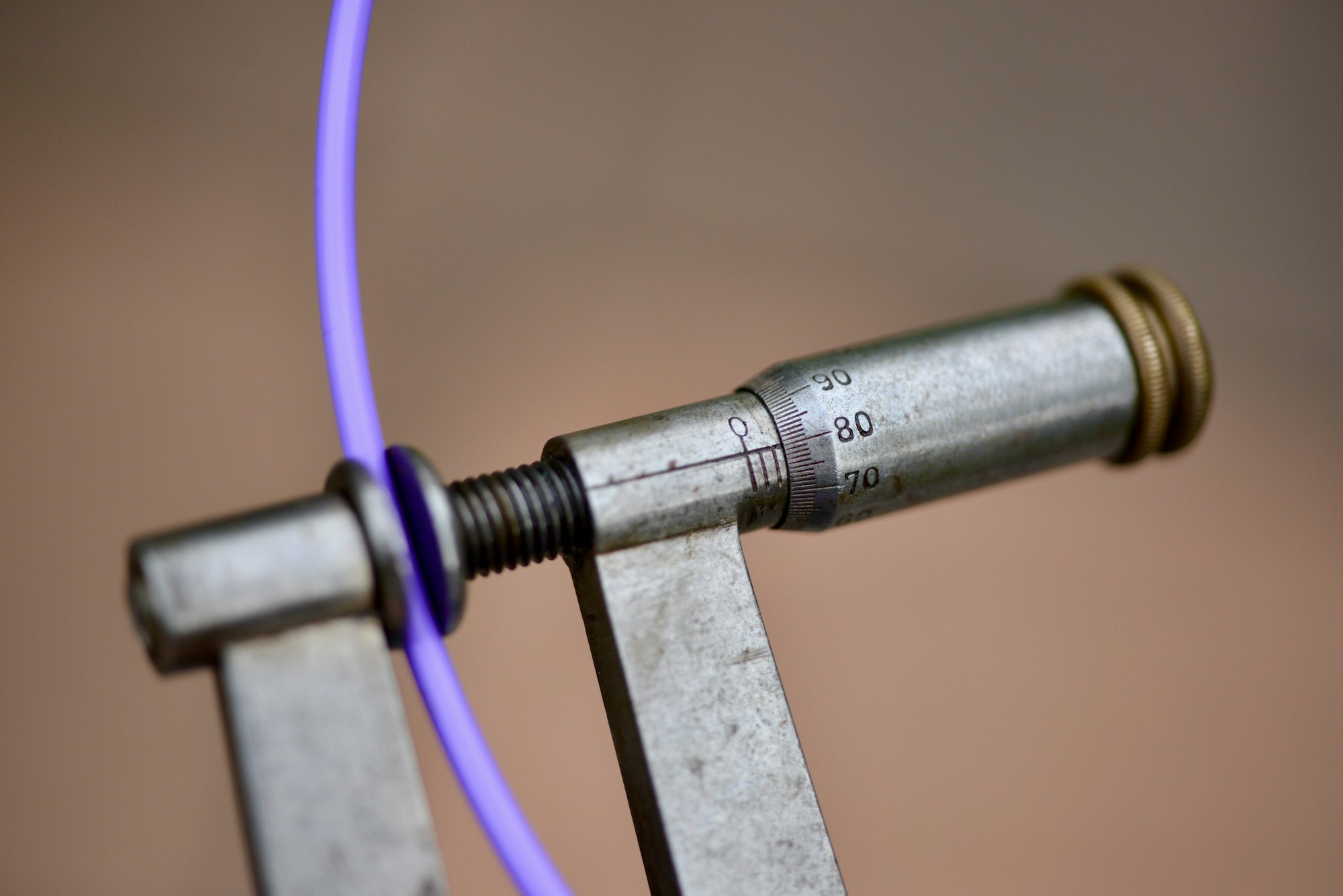

How to measure length using a micrometer screw gauge
- Read the main scale to nearest 0.5mm
- Read the additional fraction of a millimeter from the fractional scale.
- Add both the readings and obtain the thickness of the object
Measurement of volume
Measuring regular shaped objects
- Use formula to find their volumes; if it is a cube, then measure the length of one side and multiply it by 3
Measuring irregularly shaped objects
- Use displacement method:
- Pour some water in the measuring cylinder and record its volume (V1).
- Submerge the object in the water.
- Record the reading of the water level in the cylinder (V2).
- Use the formula Vx=V1-V2 to find the volume of the object.
Measuring liquids
Use a measuring cylinder
Density
Density is the ratio of mass to volume for a substance
Measuring density
The most accurate way to calculate the density of any solid, liquid or gas is to divide its mass in kilograms by its volume (length × width × height) in cubic meters.
Density can be found using the equation:
D = M / V
where D -> Denisty
M -> Mass
V -> Volume
The unit for density is kg/m3.
Denisty Facts
- Gases have lower densities than liquids
- Density of water is 1000kg/m3
- Density depends on the composition of the material
- The amount of a metal in an alloy can be found by measuring it’s density
Density simulator
Understand density better. Use the simulator below to apply what you have learnt in this section to get some hands on learning. Make sure to take notes on anything that particularly stands out to you.
Common Densities
Here are a few densities of some common objects (in kg/m^3)
Wood. - 0.40
Gasoline - 0.68
Apple - 0.83
Ice - 0.92
Human - 0.95
Water - 1.00
Glass. - 2.70
Diamond. - 3.51
Titanium. - 4.50
Steel - 7.80
Copper. - 8.96
Lead. -11.34
Gold. -19.32
Measuring time
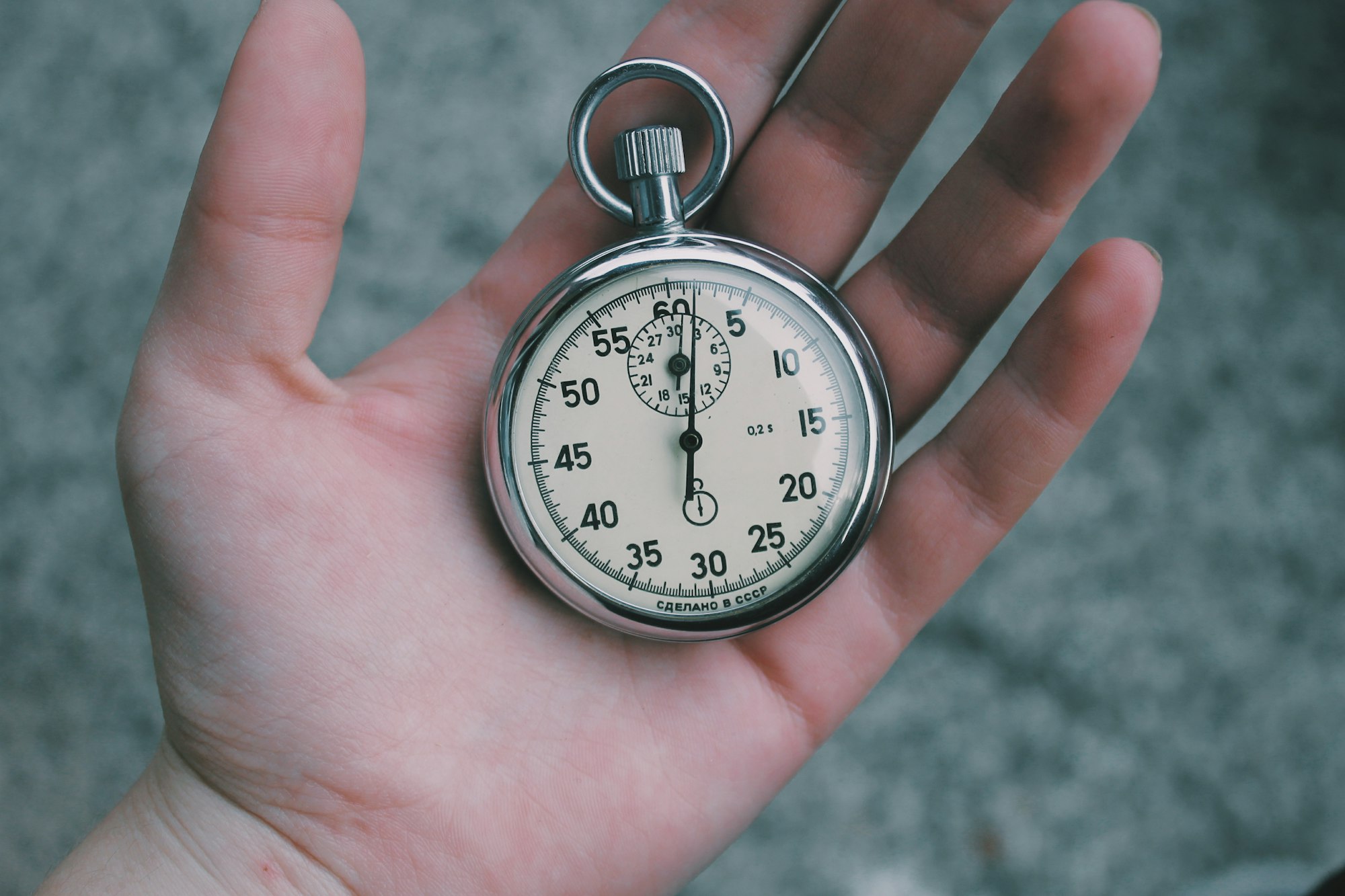

Time can be measured in a laboratory using stopclocks and stopwatches. Measuring time is essential; especially when calculating speed and acceleration.
For improving the accuracy, light gates and electronic timers are used during experiments involving motion.
Intervals of time can be measured using a pendulum:
- A pendulum can be made to swing 10 times with a stopwatch running simultaneously.
- The time taken for one swing can be found out by dividing the total time for 10 swings by 10.
Scalar and Vector quantities
- Forces can be represented using arrows because they act in a particular direction and have a magnitude as well.
- This means that forces are vector quantities.
Here are some scalar and vector quantities:
Scalar Quantities:
* Speed
* Mass
* Energy
* Density
* Temperature
Vector Quantities
* Velocity
* Force
* Weight
* Acceleration
***this is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using igcsepro.org! we hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you.