People and Business

Motivation
Reasons for people working:
- Standard of living: Earning income satisfies their needs and wants.
- Security: A job means that they can always maintain or grow their standard of living.
- Experience and status: Working improves skills and gives a reputable title in society.
- Satisfaction: People work for the satisfaction of having a job.
Motivation is the reason why employees want to work hard and effectively for the business. Money is the main motivator, but there are other factors of motivation, such as social needs and esteem needs. Motivating workers is crucial as their productivity and effectiveness increase. They become less absent and are less likely to leave the job. This increases the firm's output, leading to higher profits.
Motivation Theories
F.W. Taylor:
Taylor based his ideas on the assumption that workers were motivated by personal gains, mainly money. He believed increasing pay would increase productivity and output. He introduced the piece-rate system, where workers get paid for the number of outputs produced. However, this theory is not accurate as other motivators, such as quality of work, are important.
Maslow's Hierarchy
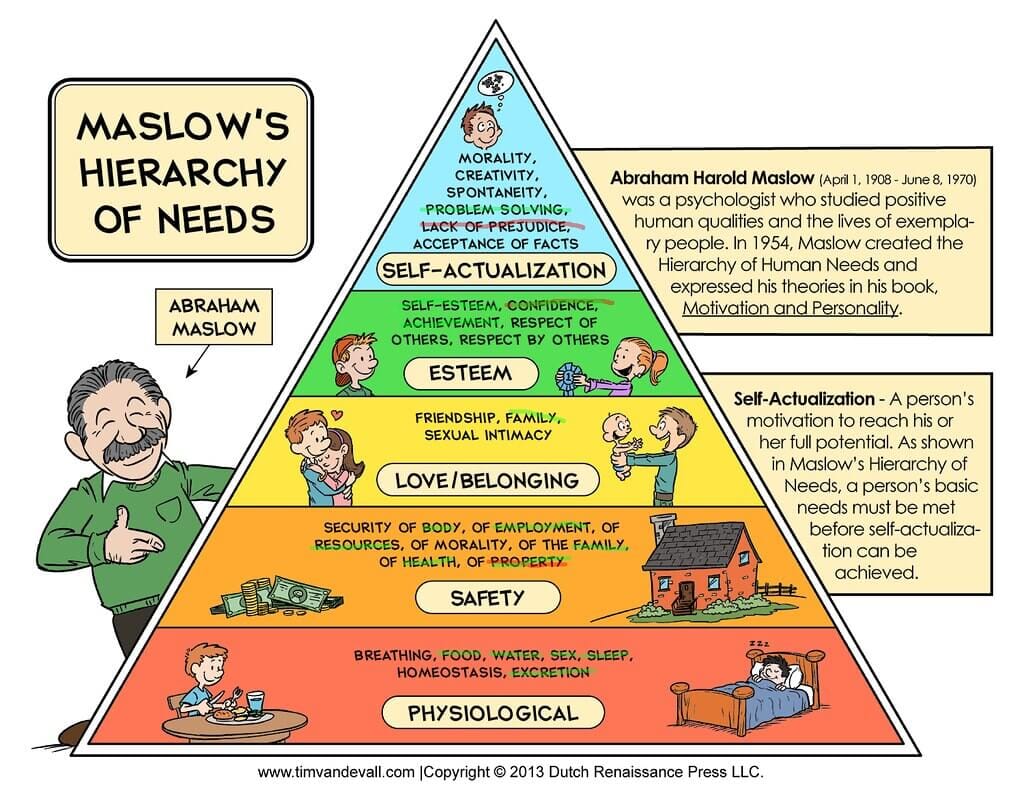
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs shows that employees are motivated by each level of the hierarchy. Managers can identify the level of their workers and take action to advance them to the next level. This theory doesn’t apply to every worker, as some may not require social needs but prefer recognition from their seniors.
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory:
Herzberg’s theory suggests people have two sets of needs: basic animal needs (hygiene factors) and psychological growth needs (motivators). Hygiene factors need to be satisfied first, but they do not act as motivators. Motivators will drive workers to work effectively.
| Hygiene Factors | Motivators |
|---|---|
| Status, Security, Work Conditions, Salary, Relationship with Staff | Achievement, Recognition, Promotion, Personal Growth |
Motivating Factors

What motivates people to work? Is it just money? What is money? Some paper our governments tell us that has some 'value' to buy things? Ok, ok- I'll stop before this becomes too existential :D. I can't help myself sometimes. Anyway, let's continue.
Financial Motivators 💴
- Wages: Paid weekly. Calculated as Time-Rate or Piece-Rate.
- Salary: Paid monthly or annually.
- Commission: Payment based on a percentage of sales made.
- Bonus: Additional amount paid for good work.
- Performance-related pay: Based on performance appraisals.
- Profit-sharing: A proportion of the company's profit is distributed to workers.
- Share ownership: Shares in the firm are given to employees to increase loyalty.
Non-Financial Motivators 😇
- Company benefits (transportation, insurance, etc)
- Free healthcare (health checkups, dental & vision checkups)
- Paid time off
- Loyalty to the Company
Job Satisfaction 😊
It is the enjoyment derived from feeling you’ve done an excellent job. (psst. You are doing a good job right now. Keep going!)
Job Rotation 🔁
Involves workers swapping around jobs and doing a specific task for a limited time, then changing again. This increases the variety of work and makes it suitable if a worker is absent/ill.
Job Enlargement 📚
Extra tasks of a similar level are added. These tasks do not add responsibility but make the work more interesting.
Job Enrichment 💪
Involves adding tasks that require more skill and responsibility to a job. This motivates workers to carry out extra tasks effectively.
Team Working 👥
A group of workers are responsible for a particular process, making decisions as a team and organizing tasks collectively.
Opportunities for Training and Promotion 📈
Providing training or promotion opportunities motivates workers to be more efficient.
Organizational Structure
Refers to the levels of management and division of responsibilities within a business.
| Advantages of Short Chain of Command | Disadvantages of Short Chain of Command |
|---|---|
| Communication is quicker, top managers are less remote, delegation is encouraged. | Managers could lose control, less opportunities for promotion leading to turnover. |
| Advantages of Long Chain of Command | Disadvantages of Long Chain of Command |
|---|---|
| Managers can manage easier, more opportunities for promotion. | Communication is slow, top managers are remote from lower employees. |
Management

- Planning: Setting aims and targets.
- Organizing: Allocating resources and responsibilities.
- Coordinating: Ensuring departments coordinate to achieve aims.
- Commanding: Leading and supervising employees.
- Controlling: Evaluating employee performance.
Delegation
Delegation involves giving subordinates the authority to perform tasks on a higher level.
| Advantages to Managers | Advantages to Subordinates |
|---|---|
| Lowers workload, helps measure efficiency. | Makes work more interesting and increases job satisfaction. |
Leadership Styles
- Autocratic: Managers make all decisions.
- Democratic: Employees are involved in decision-making.
- Laissez-faire: Employees make their own decisions with little managerial oversight.
Trade Unions
Trade unions are groups of workers who negotiate for better working conditions and can take industrial action if necessary.
Role of HR Department

- Recruitment and selection
- Wages and salaries
- Industrial relations
- Training programmes
- Health and safety
- Redundancy and dismissal
Recruitment
The recruitment process involves identifying the need for a new employee, advertising the vacancy, and selecting the best candidate through interviews.
| Internal Recruitment | External Recruitment |
|---|---|
| Saves time and money, person is already known to the business. | New skills and ideas introduced, can motivate workers. |
Training
- Induction Training: Introduction to the firm and its procedures.
- On-the-job Training: Watching a more experienced worker do the job.
- Off-the-job Training: Training outside of the workplace.
Workforce Planning
Workforce planning ensures the business has the necessary workforce for the future. This includes downsizing through dismissal or redundancy.
Legal Controls over Employment Issues
Governments introduce laws to protect employees from unfair treatment, such as unfair dismissal, wage protection, and health and safety regulations.
Effective Communication
Communication is key for effective business operations. It involves a sender, medium, receiver, and feedback.
Communication Methods

- Verbal: Face-to-face, telephone conversations.
- Written: Letters, memos, emails.
- Visual: Diagrams, charts, videos.
Factors Affecting Communication
Factors such as speed, cost, importance of written records, and feedback affect the choice of communication method.
Communication Barriers
These are factors that prevent effective communication, such as language barriers, unclear messages, or poor listening skills.