Marketing

Definition
Marketing is the management process for identifying, satisfying, and anticipating consumer requirements.
Marketing ensures to:
- Identify Customer Needs
- Satisfy Customer Needs
- Maintain Customer Loyalty
- Gain information on Customers
- Anticipate changes in Customer Needs
Marketing objectives ensure:
- Raise awareness of their product
- Increase sales and revenue
- Increase market share
- Enter new markets
- Improve existing products
Customer spending patterns may change due to change in:
- Tastes and preferences
- Technology (Outdated products become no longer wanted)
- Income
- Ageing population
Markets have become more competitive due to:
- Globalization
- Improvement in transportation
- E-Commerce/Internet
Businesses can respond to changes in spending patterns by:
- Maintaining good customer relationships
- Keep improving existing products
- Introduce new products
- Keep costs low
Niche Market

A smaller segment of a large market tailored to a specific target audience.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Can focus on customers easier. | Lack of economies of scale. |
| High price due to low competition. | Over-dependence on one product. |
| Firms can thrive in niche markets. | Little profit due to small customer base. |
Mass Market

The product is sold to the entire market, with no specific target audience.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Large number of sales. | More competition. |
| Opportunities for growth. | Prices may be lower due to competition. |
| Economies of scale (purchasing). | Difficult to survive if new. |
Market Segmentation
The process of dividing the market into groups/segments based on characteristics such as age, location, gender, income, etc.
- Increased opportunities for sales
- Cost-effective, as focus is on a specific group
Product-Oriented Business
Firms produce the product first and then try to find a market for it, focusing on quality and price.
Market-Oriented Business
The firm conducts market research to see what consumers want and then produces accordingly, setting a marketing budget.
Market Research
The process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market or product. It helps businesses understand customer preferences, pricing, and potential profits.
Market Research is needed because:
- To know if the product will sell successfully
- To know how to price the product
- To know if the product will profit
Primary Market Research
The collection of original, first-hand data directly from customers.
| Method | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Sample | People are selected randomly. | Everyone has an even chance of being chosen. | Unclear answers may be given. |
| Quota Sample | Selected based on certain characteristics. | More accurate information may be given. | Questions may be unclear if not detailed enough. |
| Questionnaires | Data collected face-to-face or online surveys. | Detailed information can be collected. Online Surveys are cheap. Customers opinion can be collected | Unclear questions can lead to unreliable answers. Time-Consuming. Expensive |
| Interviews | Ready-made questions for interviewees. | Explanation can be provided. Body language and detailed responses can allow an accurate conclusion to be formed. | The Interviewer could force the interviewee to answer in a specific way. Time-consuming, expensive. |
| Focus Groups | Group discussion about the product. | Detailed information provided. | Opinions can be influenced by others in the group. Also, it is time-consuming and expensive. |
| Observations | Can take the form of recording, watching, or auditing | Inexpensive. | Information collected might not be detailed enough |
Secondary Market Research
Data already available from internal or external sources, such as government statistics, newspapers, and the internet.
Marketing Mix (4 P's)
Refers to the different elements involved in the marketing of a product or service: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
Product

Product is the good or service being produced and sold in the market. These include:
- Consumer Goods
- Consumer Services
- Producer Goods
- Producer Services
A successful product satisfies customer needs, stands out, and is reasonably priced.
Brand image: An identity given to a product that differentiates it from competitors.
Importance of Brand Image
- Helps Customers recognize firm’s products easier
- Easier to launch if Brand Image is well-known
- Can charge higher if Brand Image is well-known
Brand loyalty is when customers keep buying the same brand continuously instead of switching over to competitors’ products.
The process of developing a product
1. Brainstorm and generate ideas
2. Select best ideas
3. Decide if the market for the product is big enough for it to be a success.
4. Develop a Prototype (also known as a minimal viable product or MVP)
5. Test Launch to a small pool of beta users
6. Launch Product if successful
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increases potential for sales | Market Research is Expensive and Time-Consuming |
| Creates USP as an innovative product has been introduced | Investments can be expensive |
| Reduces risks due to market research |
Importance of Packaging
- Protects the product
- Provide information about the product
- Helps customers recognize the product from the Brand Logo and Name.
Product life cycle
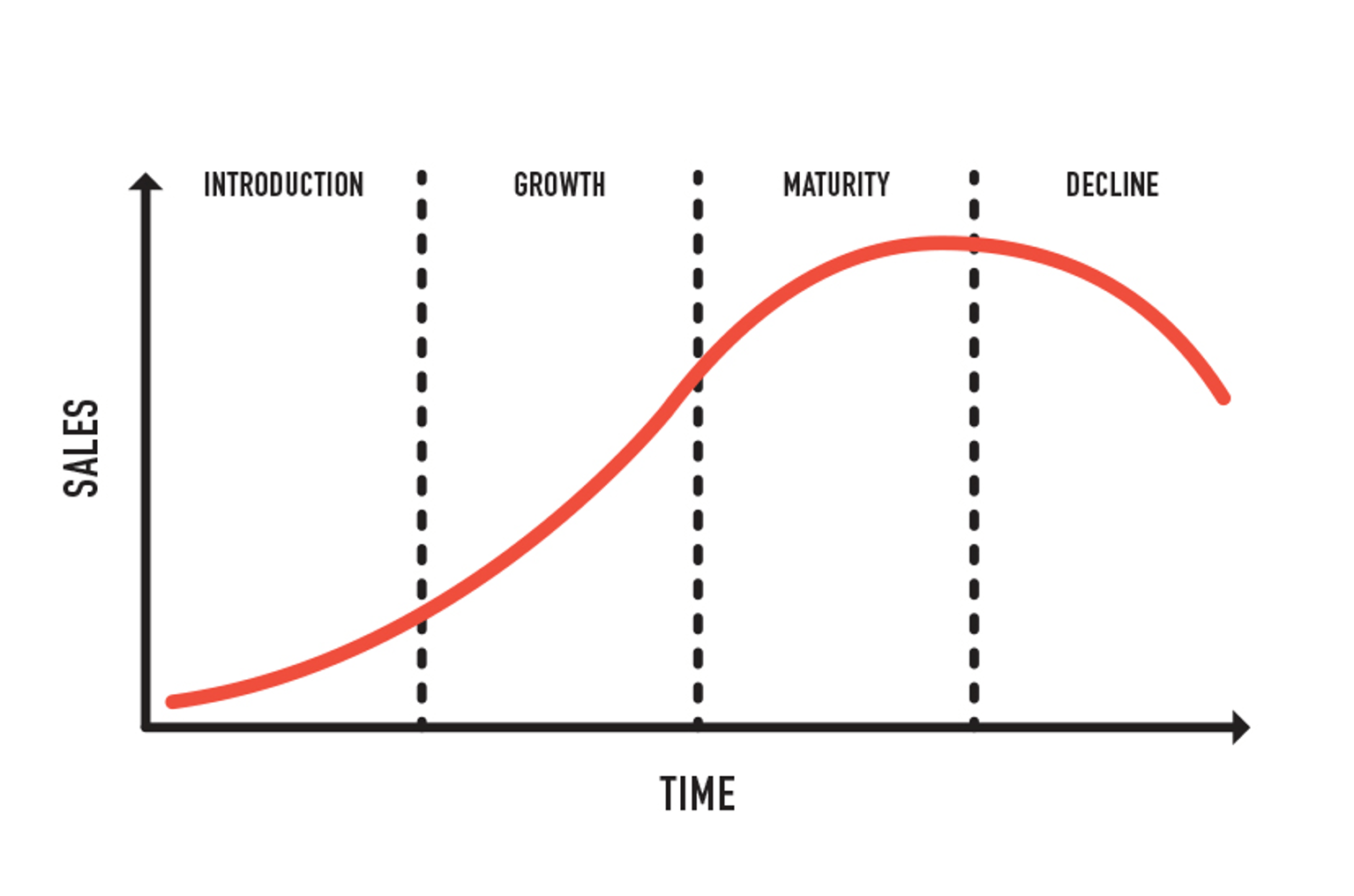
| Introduction | Growth | Maturity | Decline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Only a basic model of the product is available | Changes might be made to the product as a result of feedback from consumers | Extension strategies might be used to maintain sales | The product and packaging is not altered |
| Price | Price skimming is unique new product; market penetration pricing otherwise | Pricing may be adjusted- lower prices to attract more sales or keep a high price to maintain brand image | Competitive pricing to maintain sales | The price might be reduced – promotional selling to maintain sales |
| Promotion | High advertising activity to boost customer awareness | Promotional activity still high to continue persuading customers | Promotional activities are aimed at reminding the customers that the products are still available | Advertise the products at a lower price |
| Place | The product may be offered for sale in specially selected outlets | The product is more widely available, which helps to increase sales | The product is available for purchase through a wide distribution network | The product is only available in profitable outlets |
Extension strategies:
These are techniques used to keep products in the market. The ways in which this can be done are:
- By entering new markets
- Increasing advertising (although this is not sustainable in the long term)
- Redesign Product
- Introduce Improved Version
Price

The amount of money consumers are willing to spend, and producers are willing to sell for.
| METHOD | DEFINITION | ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost-Plus | Is the manufacturing cost plus a profit mark-up. |
|
|
| Penetration | Price is set lower than competitors' price to enter new markets. |
|
|
| Price Skimming | Price is set high for a new product on the market. |
|
May backfire if competitors use competitive pricing. |
| Competitive | When the product is priced in line or just below competitors prices. |
|
|
| Dynamic | Price depends on demands and external factors. | ||
| Promotional | Product is sold at a low price for a short period of time. |
|
|
| Psychological | The price is set to attract the customers' attention and manipulate them. Below the whole number usually. |
|
|
Price ELASTIC: The product has many alternatives.
- Chocolate
- Cars
- Groceries
Price INELASTIC: The product has no alternatives.
- Electricity
- Water
- Natural Gas
Place (Distribution)

Refers to how a product reaches consumers. Factors include the type of product, location of customers, competitors, and frequency of purchase.
| Distribution Channel | Explanation | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer to Consumer | The product is sold to the consumer straight from the manufacturer. |
|
|
| Manufacturer to Retailer to Consumer | The manufacturer will sell its products to a retailer who will hold large stocks to sell to the consumer. |
|
|
| Manufacturer to Wholesaler to Retailer to Consumer | The manufacturer will sell its products in bulk to the wholesaler and the retailer will buy in small quantities from the wholesaler which would then be sold to the consumer. |
|
|
| Manufacturer to Agent to Wholesaler to Retailer to Consumer | The manufacturer will sell their products to an agent who specialises in foreign markets. The Agent will know the best wholesalers to sell to. |
|
|
Factors affecting where consumers buy products:
- The Type of product it is.
- The Location of the customer.
- Where competitors are located.
- How often is the product purchased?
Promotion

Activities to inform and persuade customers to buy a product. It can be informative or persuasive. Types of promotion include:
- Advertising (TV, radio, newspapers, billboards)
- Sales Promotions (BOGOF, free samples)
- Point-Of-Sale Displays
E-Commerce
The use of the internet to sell and market goods online.
- Advantages: Cheaper long-term, larger customer base, increased profits due to globalization.
- Disadvantages: Increased competition, no personal communication, and online security issues.
Marketing Strategy
A plan that combines the four elements of the marketing mix to achieve marketing objectives and profits.
Legal Controls on Marketing
These controls protect consumers from being sold faulty goods, prevent exploitation, and ensure honest advertising.
Globalization in Marketing
Businesses globalize to increase sales, revenue, and profits, gain potential customers, and access cheaper raw materials. However, challenges include language and cultural differences, lack of market knowledge, and economic differences.