Human Influences on Ecosystems

An Overview
The Earth- an exceptional planet isn’t it?
So why do you think life can exist on earth? It’s simple! We’ve got the right distance between the sun and our planet which leads to an appropriate surface temperature on earth. We have also fortunately got the right composition of gases in the atmosphere and the unique presence of water. These are just a few factors from the many!
Earth- Who rules the earth? Mother Nature? Certainly not. The earth is now reined under the bloodthirsty monarchy of us- the humans!
Food Supply

One reason for the increase in our population is food production. Food is produced majorly by growing crops and breeding livestock.
Factors that led to an increase in food production:
- Advanced agricultural machinery such as tractors and combine harvesters have enabled farmers to cultivate larger areas of land in shorter time
- Chemical fertilisers containing mineral ions have been used to improve the land’s fertility and hence it’s yield
- Insecticides have been used to destroy pests that could affect the yield and quality of the produce
- Herbicides (Weedkillers) have been used in order to destroy weeds that compete for minerals, soil, water and sunlight with the crop plants; this leaves enough space for the crop plant and thus improves the yield
- Selective breeding has been practiced which has developed new and improved varieties of plants and animals
- For example, selective breeding has produced crop plants that grow in poor soil and plants that are resistant to diseases
- Use of satellites to monitor crop development and monitor crop diseases
- Use of antibiotics, hormones and artificial insemination techniques in intensive livestock production.
Monoculture
Monoculture is the cultivation of a single variety of a crop plant over a large area.
Negative impacts of Monoculture
- Reduces species diversity of an ecosystem
- Can lead to an increase in populations of pests as availability of food increases for them
- Insecticides sprayed on the pests may not be selective and may be persistent
- Insecticides can damage other organisms in the environment as well and thus cause harm to the ecosystem
- Insecticides may even lead to the development of resistance in the insect pests
Solution: Farmers can use mixed cropping. This means that different patches of land will be covered by different crop plants.
Benefits of Mixed Cropping
- Species diversity in the ecosystem may increase
- Pests may find it difficult to spread from one patch to other
- This decreases the number of insect pests
- Thus they need to spray less insecticides
- Hence will benefit species diversity in that ecosystem.
Intensive livestock production

In developed countries, large numbers of livestock are kept in smaller areas. This is known as intensive farming.
Farmers use:
- High energy food
- A suitable room temperature
- Antibiotic doses
And give them to the livestock so that their growth rates maximise and the farmer yields greater amounts of meat, milk, wool, etc.
Disadvantages of intensive livestock production:
- Welfare issues between the livestock may emerge
- Diseases can spread easily
- Antibiotic resistance may develop if they are given antibiotics
- Waste from intensive farming units can pollute nearby waterways
- Waste from intensive farming units can cause eutrophication
Factors affecting world food supplies

There is not always enough food available in a country to feed the people living there. A severe food shortage can lead to famine.
It has been calculated that more than enough food is produced on Earth to provide every single person with more than enough for their needs. Yet many people do not get enough food.
The fundamental problem is that food is distributed unequally on our planet: while some parts of the world produce more than enough food for the people that live there, in other part of the world not enough food is produced.
- Although large amounts of food are transported from one country or area to another, this is still not sufficient to supply enough food to everybody.
- If food becomes expensive, many people may not be able to afford to buy it.
Famine can occur for many different reasons:
- Climate change and natural disaster such as drought and flooding that prevent crops from growing.
- Increasing population: population may grow so large that the land on which they live can no longer provide enough food for them.
- Wars may prevent people to grow crops and thus this leads to famine
Habitat Destruction
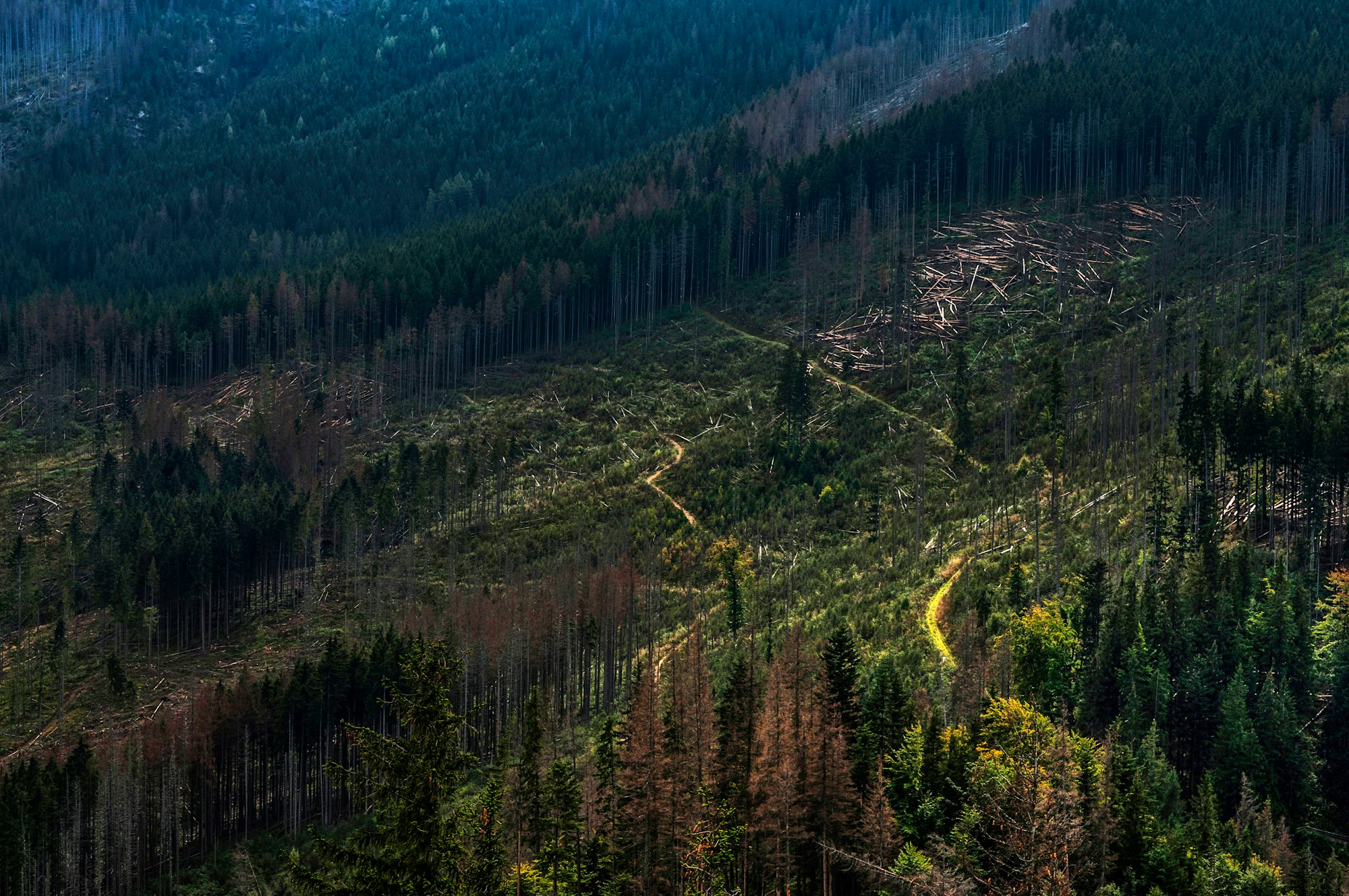

Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of large areas of forest.
Reasons why deforestation occurs
- To clear up land for farming.
- To clear up land for construction and building roads.
- To clear up land for timber for construction, furniture and fuel.
- To clear up land for mining minerals or other natural resources
Effects of deforestation on the environment
- Deforestation leads to fewer trees, resulting in lesser natural habitats for animals living there
- Deforestation can cause reduction in food resources and breeding grounds of animals and can thus result in their extinction!
- Deforestation also disrupts food webs and decreases species diversity.
- Removal of trees means there are no roots to hold the soil, which results in the top soil getting washed away, and causing soil erosion. Desertification can eventually occur as the topmost and most fertile layer of soil is washed away and the land becomes barren.
- As there are no roots to hold the soil, the top soil may be washed away into nearby waterbodies which can become silted and can eventually overflow causing flooding.
- Deforestation also causes an increase in the greenhouse effect by increasing the volume of carbon dioxide in the air (as there are lesser trees to absorb carbon dioxide)
- Deforestation also affects the water cycle; as there are lesser trees, lesser water vapour is produced through transpiration and thus gradually the air becomes drier leading to less rainfall.
Marine Pollution and Oil Spills

Often, there are massive oil spills in oceans and incidents where undersea oil wells leak.
- Oil is less dense than water and thus the leaked oil accumulates at the top of the ocean, covering a large area.
- As it covers a large area, it prevents sunlight from reaching the marine plants below, hence restricting photosynthesis.
- This soon disrupts all food chains and webs as every primary consumer is dependent on these producers for food.
- Along with that, sea birds also get damaged as they may swallow some oil while hunting for fish. This can poison and kill them, resulting in a decline in their populations.
Pollution

Eutrophication
Damage by eutrophication can be done in 2 ways:
- By spraying fertilisers or applying too much of manure
- By dumping untreated sewage into water bodies
Eutrophication done by spraying fertilisers or applying too much of manure:
Farmers often use a lot of fertilisers and manure in order to maximise their crop’s yield. But doing this can destroy an entire aquatic ecosystem by eutrophication!
- A farmer sprays a lot of fertilisers and manure on their crops.
- When it rains, all the sprayed fertiliser is washed out into nearby water bodies, such as a lake.
- Small populations of algae living on the surface of the lake start to reproduce intensively as they get an extra source of nutrition from the washed out fertilisers.
- Soon the algae population is so large that it covers the surface of the lake!
- This is known as algal bloom.
- When the algae die, they are decomposed by aerobic bacteria.
- The aerobic bacteria consume the dissolved oxygen in the lake as they decompose the algae.
- This leads to the lake having no dissolved oxygen.
- The fish and other aquatic animals die as a result the entire aquatic food web gets disrupted.
- This is how spraying fertilisers can cause eutrophication.
Eutrophication done by dumping untreated sewage into water bodies:
- A truckload of sewage is dumped into a lake
- There are many organic compounds in the sewage such as nitrates and phosphates.
- The sewage is decomposed by aerobic bacteria
- The aerobic bacteria consume the dissolved oxygen in the lake as they decompose the sewage.
- This leads to the lake having no dissolved oxygen.
- The fish and other aquatic animals die as a result the entire aquatic food web gets disrupted.
- This is how dumping untreated sewage causes eutrophication.
Sewage
Sewage is the untreated organic waste produced, along with household and industrial waste materials.
Effects of dumping untreated sewage:
- Eutrophication damages the water body
- Aquatic organisms get affected as the untreated waste contains pathogens
- Water borne diseases such as cholera spread rapidly and infect the people who drink the polluted water
Chemical waste
Chemical waste is all the inorganic waste disposed into water bodies. These include:
- Heavy metal compounds such as mercury, lead, nickel and aluminium
- Women contraceptive hormones such as oestrogen
- Crude oil
All these things can cause serious damage to the environment.
When heavy metal compounds are dumped into water bodies, they get accumulated in aquatic organisms through bioaccumulation and enter food chains and webs.
When humans eat organisms from these polluted water bodies, all the heavy metal compounds get accumulated in the highest concentrations, causing maximum damage.
These heavy metal compounds are toxic for humans and can damage our Central Nervous System (CNS)
Contraceptive pills and chemical waste
Females often take contraceptive hormones as a measure of birth control. One such hormone is oestrogen. These hormones are excreted out of the body, dissolved in urine. When the urine containing women contraceptive hormones enter water bodies, they can cause:
- A decrease in the number of sperm produced by male fish
- A change in gender of male fish
- A decrease in the number of fish born
- A decrease in the number of egg cells produced by female fish
Acid Rain

The greenhouse effect
There are some gases in the atmosphere which prevent infrared radiation pass through them. These gases are known as greenhouse gasses. Greenhouse gasses are extremely important in regulating the surface temperature on earth. Without the greenhouse effect, the surface temperatures would have been too cold for life to exist..
- Electromagnetic radiation with short wavelength enters the atmosphere
- This radiation strikes the earth’s surface and reflects back in the form of infrared radiation with a shorter wavelength towards the atmosphere.
- Most infrared radiation with a shorter wavelength is stopped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
- This causes the heat in the infrared radiation to remain on Earth
Enhanced greenhouse effect
However in the past century, due to the industrial revolution the amount of greenhouse gas emissions have increased leading to the enhanced greenhouse effect taking place.
The major difference between the greenhouse effect and the enhanced greenhouse effect is that lesser amount of infrared radiation escapes through the atmosphere due to the increase in greenhouse gasses in the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Here is a list of some greenhouse gasses:
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- CFCs
- Oxides of Nitrogen
- Water vapour
Insecticides
Insecticides are chemical compounds used to control populations of insect pests such as mosquitoes.
Though an insecticide kills the insect pest, it remains in the environment and also kills other harmless animals. This was the case with a pesticide named DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) which was used to kill mosquitoes. DDT remained in the environment and was absorbed into the food chains. This lead to bioaccumulation and the concentrations of DDT in the organisms increased as the trophic levels increased. This was lethal and caused a lot of damage to organisms that it was not supposed to kill.
This means that DDT is a non-specific pesticide as well as a persistent one.
Due to these reasons, DDT is banned in most countries now.
Herbicides
Herbicides are often used by farmers to control the populations of weeds which compete with the crop plant for nutrients, space, sunlight and water.
However, when herbicides are sprayed onto the crops, they not only kill the weeds, but also can get washed away into water systems and kill the aquatic plants there. This disrupts the aquatic food chain as the consumers get affected.
Nuclear fallout
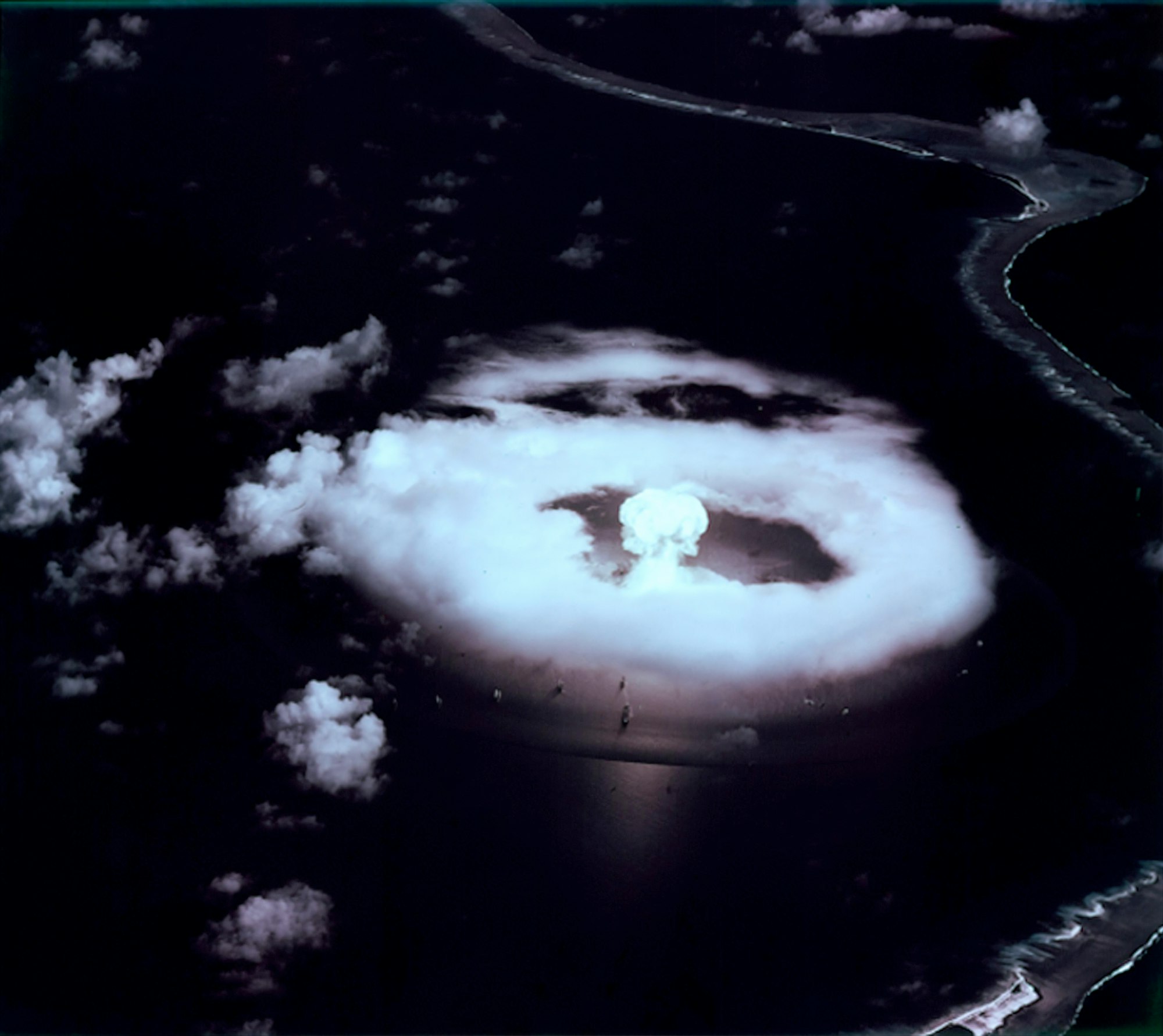

Nuclear fallout can be the result of a leak from a nuclear power station, or from a nuclear explosion. Radioactive particles are carried by the wind or water and gradually settle in the environment. If the radiation has a long half-life, it remains in the environment and is absorbed by living organisms.
The radioactive material bio-accumulates in food chains and can cause cancer in top carnivores.
Plastics and the environment
Most plastics are non-biodegradable; they aren’t broken down by decomposers when dumped in landfill sites or left as litter. This means they remain in the environment and accumulate, taking up space or causing visual pollution.
Damage caused by plastics
- Discarded plastic bottles and cans can trap small animals.
- When plastic is burned it can release toxic gases such as hydrogen chloride.
- Plastics gradually deteriorate into smaller pieces; these pieces can be consumed up by fish and birds and can make them ill.
Conservation
Conservation is the process of looking after the natural environment.
Conservation attempts to maintain or increase the population of different species living in an area, known as biodiversity.
The need for conservation of species
Many species of animals and plants are in danger of extinction, due to factors such as habitat destruction, the introduction of other species, international trade and pollution.
Loss of a species also means that its genes are lost: these may be important in the future for genetic engineering (e.g. to improve crops) and the production of useful chemicals such as medicines.
The presence of rare species can be an important source of money for poor communities, through tourism.
The species may play an important role in a food chain: its loss could endanger other species.
Ways of conserving species
- Initiating laws to protect them
- Using methods such as captive breeding and re-introduction
- Controlling human activity such as hunting, poaching, deforestation, etc.
- Educating communities over the importance of conservation
- Setting up seed banks where the seeds of millions of plant species are stored
- Re-stocking fish species by breeding them in captivity and releasing them in the wild
The need for conservation of habitats
If habitat is lost, so are the species that live in them, so habitat destruction poses the greatest threat to the survival of species.
Ways of conserving habitats
- Preach sustainable development; sustainable development is development providing for the needs of an increasing human population without harming the environment.
- Controlling factors, such as water drainage and grazing, That may otherwise contribute to destruction of the habitat
- Using laws to protect the habitat
- Reducing or controlling public access to the habitat
- Monitoring and controlling human activities such as deforestation, air pollution, marine pollution, etc. near the habitat.
The need for conservation of natural resources
Some natural resources (the material we take from Earth) are not replaceable (non-renewable). For example, fossil fuels such as coal took millions of years to form. The rate of consumption of fossil fuels is greater than the rate of formation and so, these natural resources are on a steady rate of depletion.
Ways of conserving natural resources
- Increase and promote the use of renewable energy (wind farms, solar power, hydroelectric power, geothermal power…).
- Improve the efficiency of energy use (better insulation, more efficient car engines, more public transports…).
- Grow trees specifically for fuel, then replant them as they are cut down. This will maintain the amount of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
- Recycle products such as Paper, Plastic, Metals, and Glass
This is the end of this guide. Hope you enjoyed it! Thanks for using www.igcsepro.org! We hope you will give us a chance to serve you again! Thank you!
Back to IGCSE Biology